Axial Deformation
Axial compressive strain of steel bars will tell you how much length is shortened, or conversely, it will stretch when squeezed or pulled. Power is 1 unit, cross-section 5 units and length 100 units. => Relationship between axial compressive strength and the range is 1 / 1000. This relationship existing, others are known without formula. Take a few minutes to think about this. Gravitation is 9.82 m/s2. Calculation uses generally cm unit. The calculation is based on the Newton - Gravitation - Surface Area - Figure Five combination. One feature of the calculation is the Visual Geometry, which means the figures and calculations are visually shaping the reality. The calculation image above is a calculation that represents the accession of each other names. At this point, is enough to detect the ratio of the links between them. Eventually, surface area and strength are the same meaning. Axial compression rod is inversely elongation rod. The calculation uses the value 20600 cm4 of the Modulus of Elasticity.
This is easy to remember
F = 1 kN L = 100 cm A = 5 cm2 ό = 0,001 E = 20 600 kN / cm4
Basic load is always 1 kN
Length 100 cm is easy to remenber
Deformation 0,001 cm
Beam cm
F kN ==> ==================== <== kN
ό = 100 cm x 1 kN x cm2 = 0,001 cm
20600 kN x 5 cm2
The formula calculates steel deformation and elongation, without need to understand the calculation. EPC calculation requires an output value, which is the formula does not require.
 Click on the calculation Click on the calculation
EPC Calculation
Example 1
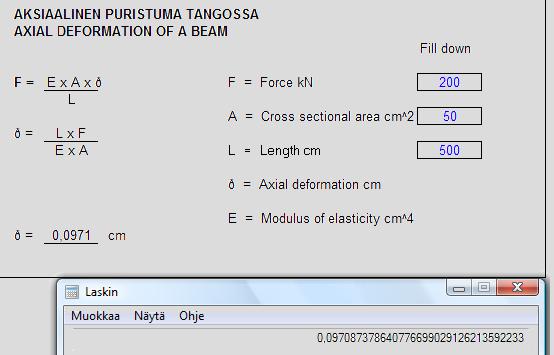
F = 200 kN => FΔ = 200 (x 1 kN)
L = 500 cm => LΔ = 5 (x 100 cm)
A = 50 cm2 => AΔ = 10 (x 5 cm2)
ό = 0,001 x FΔ x LΔ = 0,001 x 200 x 5 = 0,09708
1,03 x AΔ 1,03 x 10
Example 2
F = 1200 kN L = 800 cm A = 315 cm2 ό = ?
ό = 0,001 x FΔ x LΔ = 0,001 x 1200 x 8 = 0,1479
1,03 x AΔ 1,03 x 63
(Spread sheet calculation gives 0,1479)
Example 3
F = 0,3 kN L = 20 cm A = 1 cm2 ό = ?
ό = 0,001 x FΔ x LΔ = 0,001 x 0,3 x 0,2 = 0,000291
1,03 x AΔ 1,03 x 0,2
(Spread sheet calculation gives 0,0003)
Calculate the other cases, having the same procedure and accuracy.
21.6 2018*08:00 (919 - 779)
www.karikolehmainen.com
epcalculation@gmail.com |