Lagrangian Points
Two mutually rotating masses have near them five possible locations, where the body may remain a constant distance. Points 1 and 2 are stable positions. The satellite disturbed by an external force, it within certain limits will return to the original location. We can think the curved space-time to one kind of bowl. The space-time determines the moving masses in the space. Numbe five has a significant role in the EP-calculation, which comes up in many contexts.

Earth - Moon system or other similar system
The Earth - yellow
The Moon - green
Points 3, 4 and 5 are unstable. If the pieces in the points are harassed, they will not return back to their location. Point 1 and 2 are stable only if the largest mass of three masses is 24.94 times or more larger than the mass of the middle.
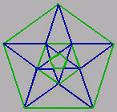 EP-calculation through visual geometry is studuing geometric patterns and number five in them. Points 1 and 2 are interesting, gathering space debris and dust. In addition, they are monitored for potential foreign civilizations sent by spy satellites, which are likely located in these locations. EP-calculation through visual geometry is studuing geometric patterns and number five in them. Points 1 and 2 are interesting, gathering space debris and dust. In addition, they are monitored for potential foreign civilizations sent by spy satellites, which are likely located in these locations.
Distance r Between Points 3 - 4
When the smaller mass (M2) is much smaller than the larger mass (M1) are the Lagrangian points L3 and L4 at approximately the same distance on both sides the smaller body.
M2 The Moon mass 7.34 x 1022 kg (the smaller mass)
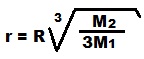
R Distance between the masses (384 400 km from the Earth to Moon)
r L3 ab. 61500 km behind the Moon L4 ab. 61500 km in front of the Moon
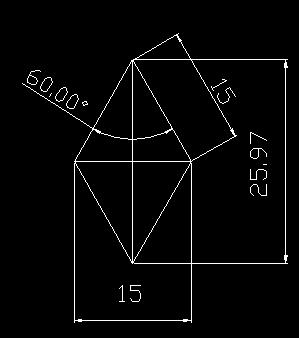
As the visual geometry, the Earth, point 1 and the Moon form an equilateral triangle, wherein angles are 60 degrees. This is standard to Lagrangian points 1 and 2.
25.97 / 15 = 1.731
SQRT 3 = 1.732, this means the distance between point is proportionally calculated.
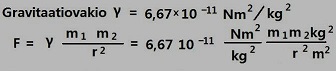
Y = the gravitational constant
The Earth mass 5.98 x 1024 kg
The Earth radius 6.37 x 106 m
The force of gravity on the Earth is eg. 9,82 m/s2. This can calculate from the formula, but this time the value is given. Insted of that we calculate the force of gravity on the Moon.
On the Moon
The formula is based in the relative weight of 1, the mass of the Moon and radius.
The Moon mass 7,34 x 1022 kg
The moon radius 1,74 x 106 m.
The force of gravity g on the Moon is 1,617 m/s2 (the golden ratio 1.618)
6.67 x 10-11 x 1 x 7.34 x 1022 = 1.6170 (The Golden Ratio 1,618)
The force of gravity on the Earth / The force of gravity on the Moon
9.82 m/s2/ 1.617 m/s2 = 6,073
EP-calculation
2 x 3.14 = 6.073
1.034
The Sun - Earth System
Points L3 and L4 are at the distance of 1,500,000 km at both sides the Earth.
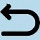
1.2.2015*23:10 (1007 - 685)
www.karikolehmainen.com
epcalculation@gmail.com |